Definition
Stack is an STL used to store and load items using the LIFO System (last in first out), which means items can be added to the end of the stack only and the last item added is the only item that can be accessed (get, edit or remove).
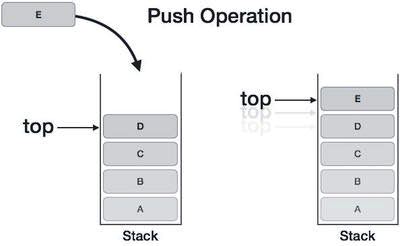
In the stack, all operations are done on one end, the right end, which is usually referred to as the "top".
Stack Operations
There are some operations used in stacks to add new items, access items in the stack, and remove items:
- Add: insert a new item to the right end of the stack (top).
- Remove: delete the last item added to the stack (the item at the top)
- Get: returns the last item added to the stack (the item at the top)
All operations supported by the stack have time complicity of O(1) so the overall complexity of the stack is O(1) the space complicity of the stack is O(n) where n is the number of items.
Example on Stack
Let's observe how the stack works when we apply the following operations in the same order they were given:
- Add 2
- Add 3
- Get
- Add 0
- Remove
- Add 1
- Remove
- Get
(1) In the beginning the stack is empty, after the first operation 2 will be added to the top of the stack
(2) After the second operation 3 will be added to the top of the stack
(3) The third operation is a Get operation and the result is the item in the top (3)
(4) The fourth operation is an Add 0 operation so 0 is added to the top of the stack
(5) The fifth operation is a Remove operation so the item at the top of the stack is removed
(6) The Sixth operation is an Add 1 operation so 1 is added to the top of the stack
(7) The seventh operation is a Remove operation so the item at the top of the stack is removed
(8) The eighth operation is a Get operation and the result is the item in the top (3)
Stack Implementation
#include Output:
Item on top is: 3
Item on top is: 3